Relativistic Symmetry
Here we examine the symmetries that exist between the specialized and generalized theories of relativity, how they affect our experience on Earth, and how they relate to the model of relativistic spatial dilation.
One mystery that has bothered me more than most was the manner in which the time dilation effects due to special relativity and general relativity are almost perfectly equivalent here on Earth. The centripetal force of the Earth's rotation is believed to be responsible for the Earth being not quite spherical, with a bulge forming near the equator. As the Earth spins, the excess time dilation at the equator due to the additional velocity created by the Earth's rotation, is almost perfectly offset by the excess gravity at Earth's poles which is a consequence of a slightly shorter radius.
Surely there must be some physics at play here that binds the rotation of the Earth to it's radius and mass density, that's really not much in question. Perhaps more profoundly, surely these to sources of time dilation must be the same.
We can start by analyzing this symmetry from the perspective of a single, simple equation:
This is to say that
Looking at this in the context of the model of relativistic spatial dilation, recall that
If we are not concerned with the new radius, but only the change in radius, the
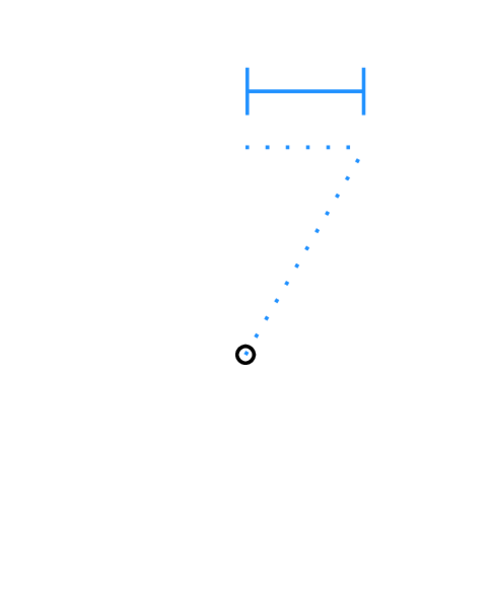
On the other side of this equation, we have the rotational velocity at the equator. If instead of a set of equations that apply uniquely to the Earth's equator, consider the following:
This is to say that the sine of the integral
Which when put together, gives
Interpretation
This result can be viewed from several perspectives. First,
The left side of this equation is more physically obvious, but interesting none the less as we integrate not just over the rotational velocity, but of all of the rotational velocities on the Earth's surface.
Lastly, this relationship is time independent. While
In relation to
This section relates closely to, but extends upon the principles covered in the article available here.
Recall that
If we take a closer look at how
While this relationship between
If this relationship exists, it must be dependent upon a body's motion in respect to the local spatial dilation. Consider the fact that
Relating this symmetry to the relationship between
This relationship appears to lend credence to the principle that allows
Footnotes
-
The principle that
-
If you have yet to read the post that summarizes the model that inspired the creation of ULLD you can find that here. ↩
-
The spatial dilation would actually radiate from that body, assuming this relationship takes place in a vacuum in empty space. However, the